Definition of ERP Accounting
An ERP Accounting Software is one that automates the tasks performed by various users in the finance department of a company. These users could be accounts clerks, accountants or managers. The software could either be installed on Cloud Servers in which case it is called Cloud ERP or ERP on Cloud.
An ERP in accounting allows you to configure the system accurately so that all the transactions are accounted for accurately and reported automatically.
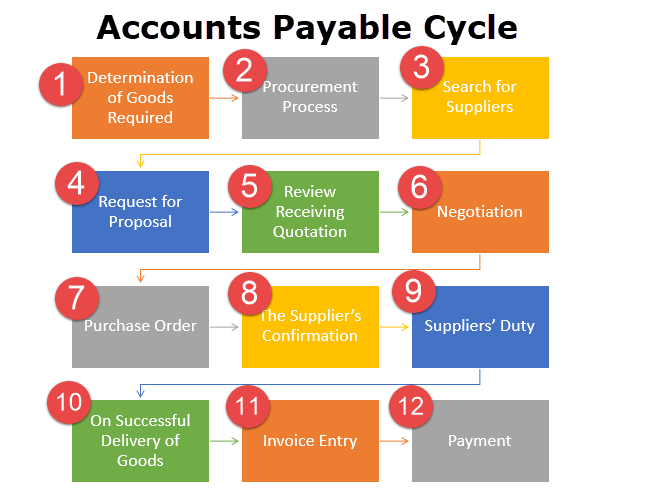
ERP Accounting Software is mostly used by the Finance department. The department has three major tasks, Corporate Finance & Treasury (CF&T), Accounting and Reporting, and Financial Control.